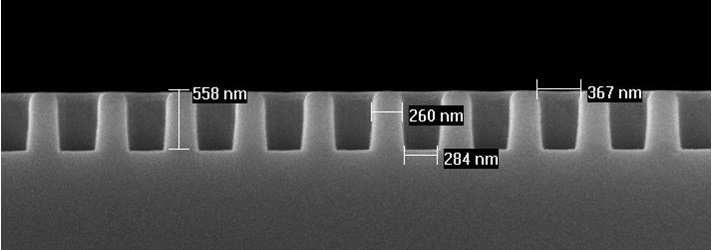
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, or SERS, is a powerful technique in the field of light measurement. Raman spectroscopy itself measures the interaction of light with matter to analyze molecular composition. The “surface-enhanced” aspect of SERS comes into play when surface roughness at the micro- and nanoscale levels amplifies the Raman signal, making it possible to detect even trace amounts of a substance.
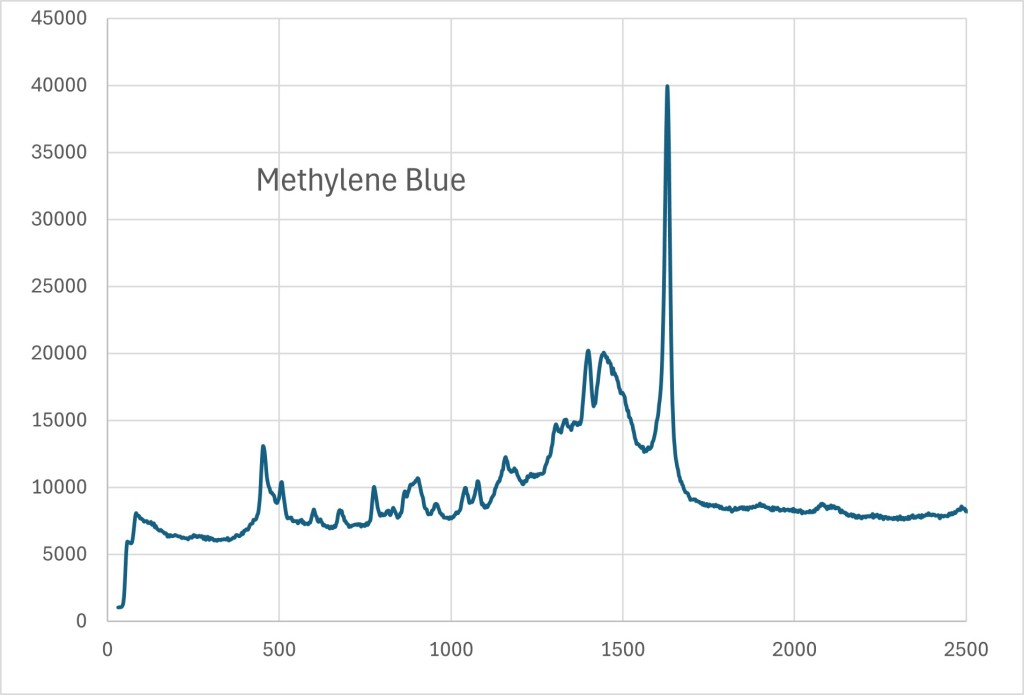
The image on the right demonstrates this capability, showing Methylene Blue detected on a nanopatterned surface using a Raman spectrometer.